Part 1: Deploying FastAPI app to AWS Lambda with Docker image
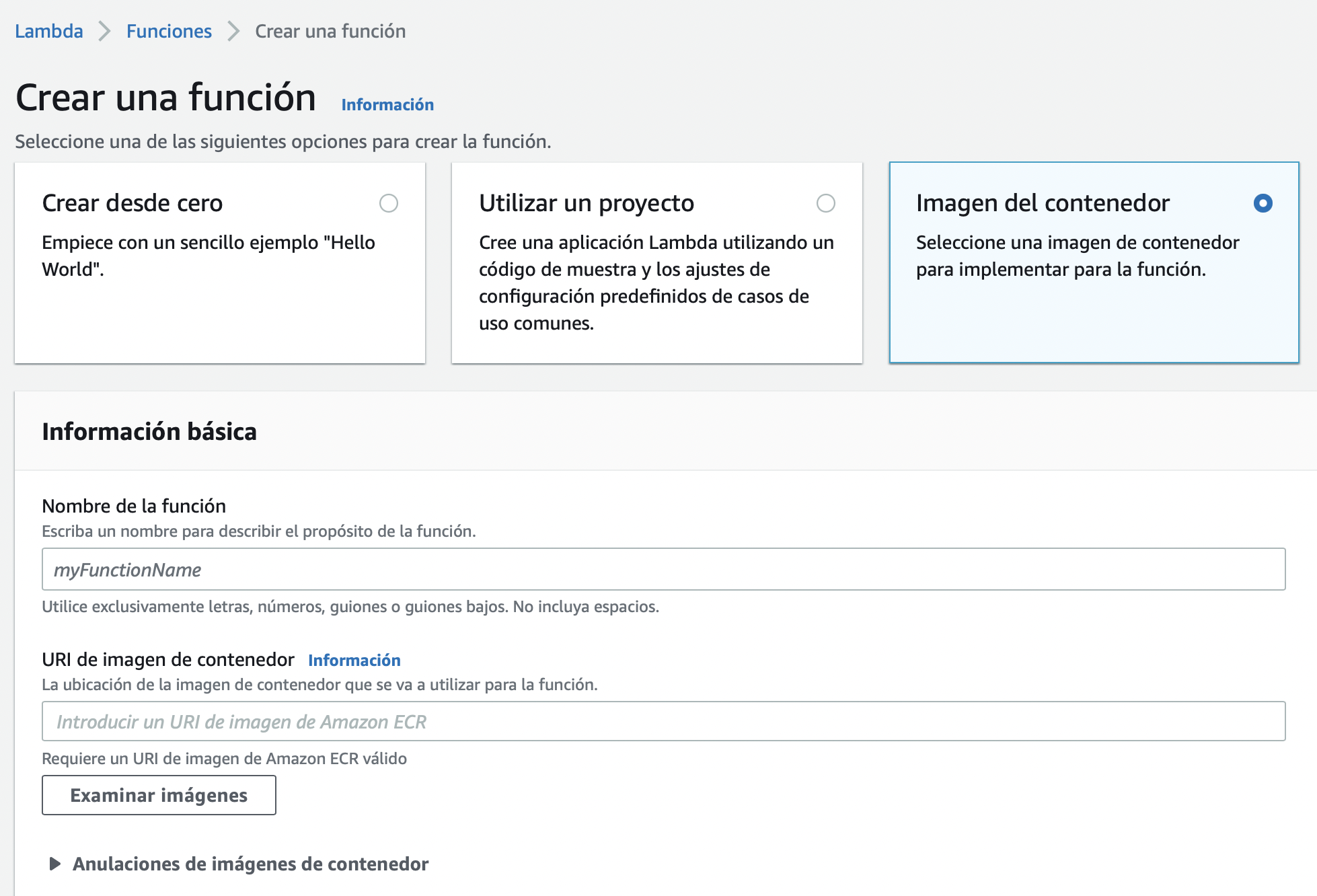
This will show how to build a Docker container that can be run by AWS Lambda from the Elastic Container Registry.
The steps to follow on AWS are currently manual - via the AWS Console and the ECR provided Docker commands to upload
images.
In future release, we will automate this release cycle using CodeDeploy, or possibly another AWS service if that turns out to be a better fit (CodePipeline? CloudFormation?)
Deploying FastAPI to AWS Lambda
Lambda allows multiple methods to provide the software artifacts to be executed as a Lambda Function. For a Python FastAPI app, the primary choices are a zip file and a Docker container image.
To deploy via zip file, follow the excellent instructions from Simon Willison at asgi-mangum
To summarize, this method uses the wrapper library Mangum to translate between AWS Lambda’s
(event, context) and ASGI’s standard HTTP interface.
AWS Lambda Runtime Interface helper
Amazon provides the awslambdaric helper library, or runtime interface client, to allow a Docker container to act as Lambda event receiver. This library can be easily added to Dockerfile and will work with Python 3.10, although not yet released on official AWS images. For the full dockerfile logic please refer to the AWS docs on PyPi. These also provide a multi-stage build to save image space.
FROM python:3.10
RUN apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y \
g++ \
make \
cmake \
unzip \
libcurl4-openssl-dev
RUN pip install \
--target ${FUNCTION_DIR} \
awslambdaric
In layman’s terms a Docker container provides an executable command interface (or none for background services) via the CMD and ENTRYPOINT directives. Lambda Functions can also overwrite these if needed.
The CMD in Docker tells whomever is “calling” the Docker container what code will actually run and with which parameters. The caller can then modify these, for example to change a default path, timeout or other configuration value. Usually, in Kubernetes for example, this is defined during engineering and seldom modified later in the deployment cycle.
Kubernetes also allows the Docker command and entrypoint to be overridden, confusingly, with it’s own Command and Args specification While confusing, both sets of directives are useful to allow custom, zonal/regional or otherwise different deployments from the same docker image, specifying values from the local execution context or infrastructure, or even date.
Lambda Entrypoint and CMD
For a Lambda function, the container should be instructed to hand control of it’s output to the runtime interface client as follows:
ENTRYPOINT [ "python", "-m", "awslambdaric" ]
CMD [ "app.module.handler" ]
Assuming that we have a file structure with python package “app” and a module “module” which provides the handler function (more on this soon!)
fastapi_lambda_app
> app
> module.py
module.py:
def handler():
return "Lambada Oh"
All set, we can now upload our Docker image to the Amazon Elastic Container Registry for use in a Lambda Function.

However, this docker image won’t know what to do when Lambda sends it’s (event, context) information, not yet.
Mangum, the Python ASGI Lambda hero
To deploy FastAPI, or any ASGI compliant Python code via AWS Lambda, all that is required is to wrapp the ASGI application with [Mangum](https://mangum. io)
Revised module.py:
import fastapi
from mangum import Mangum
app = fastapi.FastAPI(exception_handlers=home.exception_handlers)
...
FastAPI application code and paths...
...
handler = Mangum(app)
Notice, there is no call to uvicorn or any other ASGI gateway library since we just want a function that Lambda can call.
Build Docker image and upload to ECR
Once properly built and tested locally, we can upload the Lambda-ready image to ECR. This requires an existing ECR repository and appropriate AWS permissions.
docker build -t my_app .
docker tag my_app:latest <aws_account>.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my_app:latest
docker push <aws_account>.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my_app:latest
AWS Lambda Function Link
A little known feature of AWS Lambda Functions is that they can have their own URL, without the need for a Load Balancer or API Gateway to route requests into the function. This is very useful for simple website apps such as a FastAPI developer site, or any endpoint that doesn’t require heavy lifting and processing of requests.
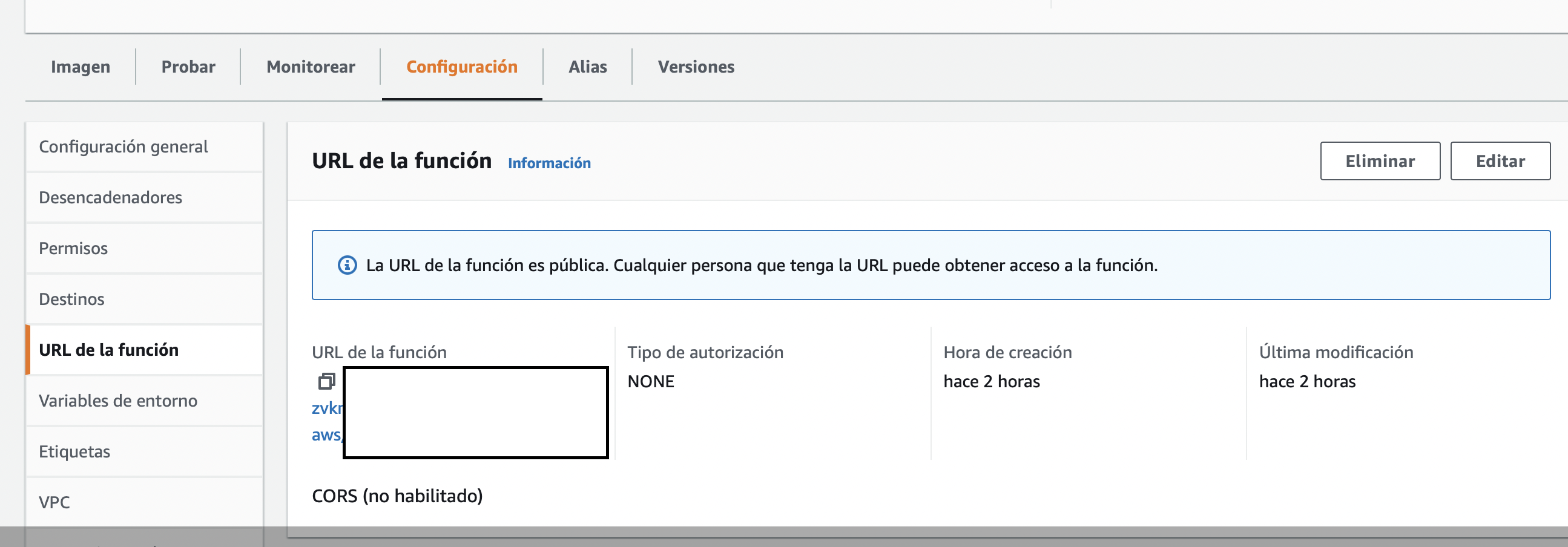
The Lambda Function link can be protected by IAM, or open to the public. This URL can then be used as the CNAM in your preferred domain management console, to route actual human users in!
Part II: Setup CodeDeploy for AWS Lambda automation?
As mentioned in part I, we might end up using CodePipeline or another service to automate our FastAPI containerized app deployments to AWS Lambda function. However, here is the setup for CodeDeploy in case it’s needed.
Deploy User for automation and DevOps responsible for CI/CD
Create an IAM group and deploy user account with the following roles and without AWS Console login access. So this user should only have an Access Key and Access Secret, but no Password. Additionally, if using SSH for CodeCommit create an ssh key for user with:
ssh-keygen
Then, upload the contents of public key file ending with <key_name>.pub to the deploy user SSH public keys. Reference:
setting-up-ssh-unixes.html
Deploy User roles and permissions
In a production scenario, the Deploy User should only have required Read access to Repos, S3, etc. For testing, allowing full access speeds up development but should be restricted later for security.
- AWSCodeCommitFullAccess
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AWSCodeDeployFullAccess
- AWSCodeDeployRoleForLambda
- AWSLambdaRole
This IAM user will be used to manage code repositories, create CodeDeploy objects such as Application, Deployment-Groups and Deployments.
CodeDeploy Service Role
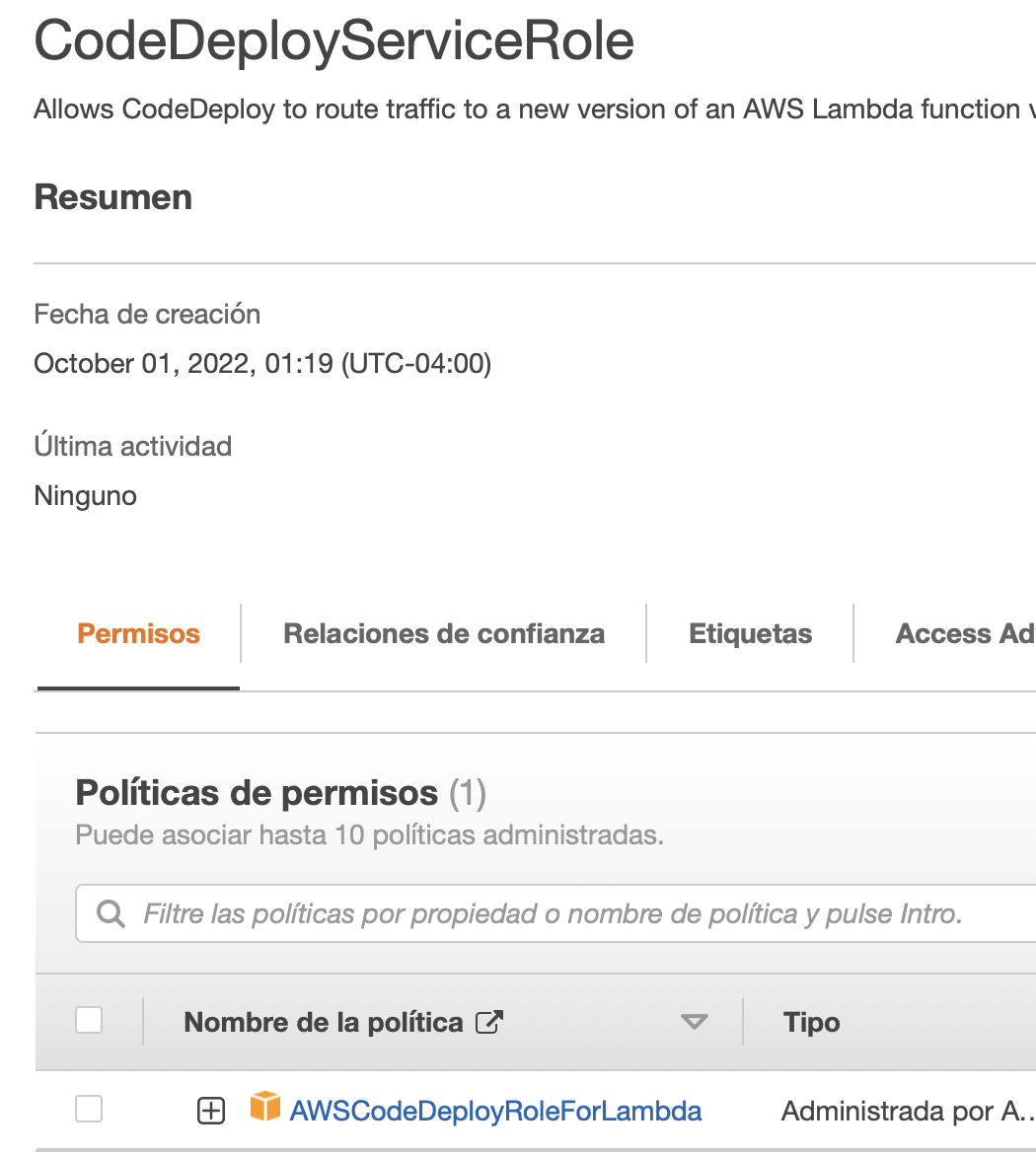
To run the actual Lambda functions and put the application into production, AWS Code Deploy requires a separate service-associated account. Create a CodeDeployServiceRole which the AWS service will use to run. This will be associated to the deployment-group upon creation.
IAM Pass Role Policy for Deploy User
Create the special IAM policy and assign it to the deploy user account to create the Deployment Group and “pass” the CodeDeploy service account permission to execute on it’s behalf.
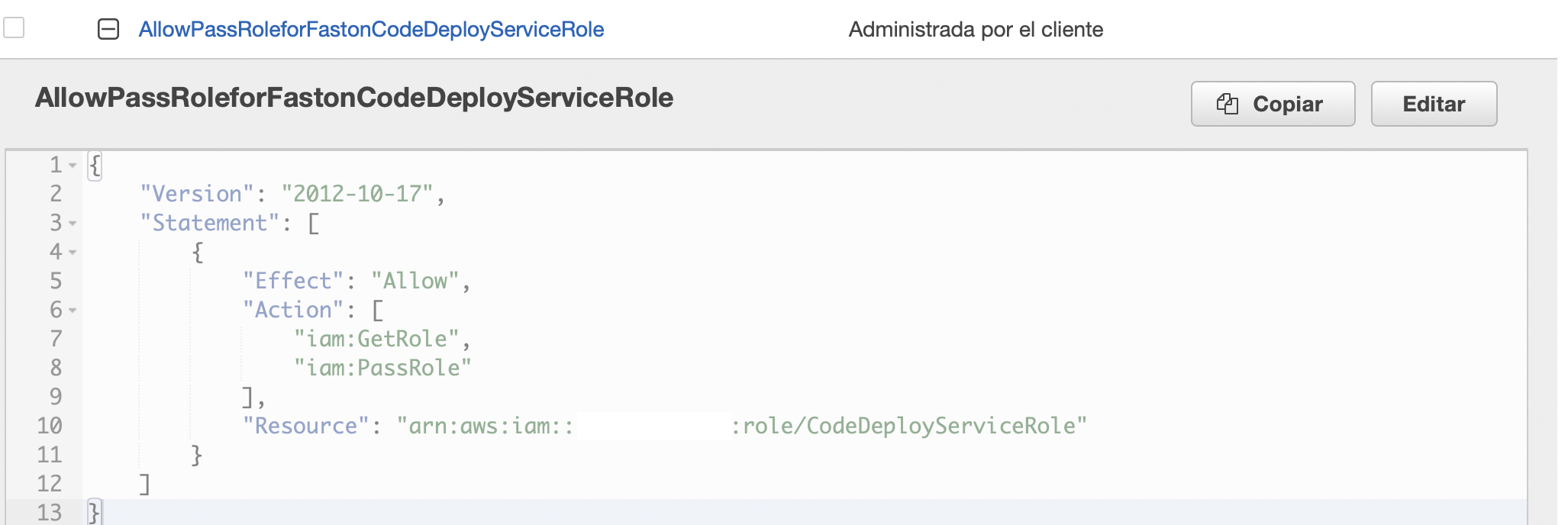
Create Policy to allow deploy user IAM-PassRole
aws command to create deployment-group
aws deploy create-deployment-group --application-name <name> --deployment-group-name <deployments_name>> \
--service-role-arn arn
:aws:
iam::<AWS account>:role/CodeDeployServiceRole
{
"deploymentGroupId": "<id>"
}